Product
Contact us




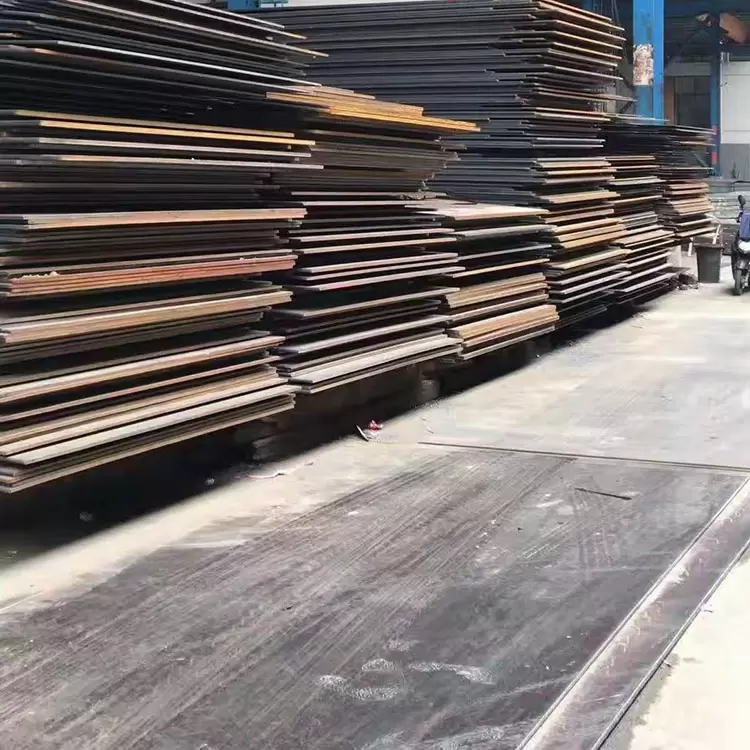
Steel processing
 0757-28908555
0757-28908555
Core Processing Techniques
Steel processing integrates various advanced technologies to meet complex design demands, with key methods including:
1. Cutting
· CNC Laser Cutting: Uses high-energy laser beams to precisely cut thin to medium steel plates (0.1–20mm), achieving tolerances as low as ±0.1mm. Ideal for intricate shapes, fine contours, and materials like stainless steel and high-alloy steel.
· Plasma Cutting: Utilizes a high-temperature plasma arc (15,000–30,000°C) to cut thicker steel (0.5–100mm) at high speeds, suitable for carbon steel, aluminum, and non-ferrous metals.
· Flame Cutting: Combines oxygen and fuel gas to melt thick steel plates (≥20mm), cost-effective for large structural components like bridge girders and industrial machinery bases.
· Water Jet Cutting: Employs high-pressure water mixed with abrasives to cut heat-sensitive or brittle materials (e.g., tempered steel), leaving no thermal distortion.
2. Forming & Bending
· CNC Press Bending: Uses hydraulic presses to bend steel plates into angles, arcs, or U-shapes with precise control over bend radius and angle (±0.5° tolerance). Critical for manufacturing frames, enclosures, and structural supports.
· Rolling: Curves steel plates into cylindrical or conical shapes (e.g., tank bodies, pipe sections) through continuous rolling, suitable for large-diameter cylindrical components.
· Stamping: Applies pressure to thin steel sheets to form shapes like brackets, panels, or automotive parts, ideal for mass production with consistent dimensions.
3. Welding & Assembly
· Arc Welding: Includes MIG (metal inert gas) and TIG (tungsten inert gas) welding for joining steel components, ensuring strong, leak-proof joints in pressure vessels, pipelines, and machinery.
· Laser Welding: Uses a focused laser beam for high-precision, low-heat welding of thin steel parts (e.g., automotive sensors, precision instruments), minimizing distortion.
· Bolted Assembly: Combines welded structures with mechanical fasteners (bolts, nuts) for modular components, facilitating on-site installation and maintenance.
4. Machining
· Milling & Drilling: Uses CNC milling machines and drill presses to create holes, slots, or threaded surfaces in steel parts, essential for fitting hinges, shafts, or connectors.
· Grinding: Polishes steel surfaces to achieve smoothness (Ra 0.8–3.2μm) or precise dimensions, critical for bearing seats, hydraulic cylinders, and other high-precision components.
5. Surface Treatment
· Painting & Coating: Applies anti-corrosive paints or powder coatings to protect steel from rust, suitable for outdoor structures (bridges, fences) and industrial equipment.
· Galvanizing: Dips steel in molten zinc to form a protective layer, extending service life in humid or marine environments (e.g., offshore platforms, marine hardware).
· Shot Blasting: Removes rust, scale, or contaminants from surfaces, improving adhesion for subsequent painting or coating.
Key Advantages
· Customization: Tailors steel components to exact design specifications (CAD drawings, 3D models), ensuring perfect fit for unique applications (e.g., 异形件 for specialized machinery).
· Precision: Advanced CNC technology ensures tight tolerances (±0.1–1mm) and consistent quality across batches, reducing assembly errors.
· Material Versatility: Processes all types of steel, including carbon steel, high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steel, stainless steel, and heat-resistant alloys, adapting to diverse performance needs (strength, corrosion resistance, heat tolerance).
· Efficiency: Integrates automated workflows (e.g., robotic welding, AI-driven nesting for cutting) to boost productivity and reduce lead times, even for complex projects.
· Cost Savings: Optimizes material usage (via nesting software) and reduces post-processing steps, lowering overall production costs.
Typical Applications
Steel processing serves as the backbone of numerous industries:
· Construction: Produces beams, columns, and custom structural nodes for high-rises, stadiums, and bridges.
· Automotive & Transportation: Manufactures chassis parts, body panels, and rail components with lightweight, high-strength steel.
· Energy & Petrochemicals: Fabricates pressure vessels, heat exchangers, and pipeline components from corrosion-resistant and high-temperature steel.
· Machinery Manufacturing: Creates gears, brackets, and machine frames with precise dimensions and load-bearing capacity.
· Aerospace & Defense: Processes high-strength alloy steel for aircraft parts, missile casings, and armored vehicles, demanding extreme precision and durability.
Choosing a Steel Processing Partner
When selecting a steel processing service, prioritize providers with:
· Advanced equipment (CNC lasers, robotic welders) and certified quality management systems (ISO 9001, ASME).
· Technical expertise in material science (matching steel grades to processing methods) and engineering design.
· Flexibility to handle small-batch prototypes and large-scale production.
· Comprehensive service (from material sourcing to final inspection) to streamline supply chains.
Steel processing transforms raw steel into functional, high-performance components, driving innovation in modern manufacturing. By leveraging precision techniques and material expertise, it enables industries to build safer, more efficient, and longer-lasting products—making it an indispensable part of the global industrial ecosystem.
RELATED PRODUCTS
Products
-
No Data




