Product
Contact us




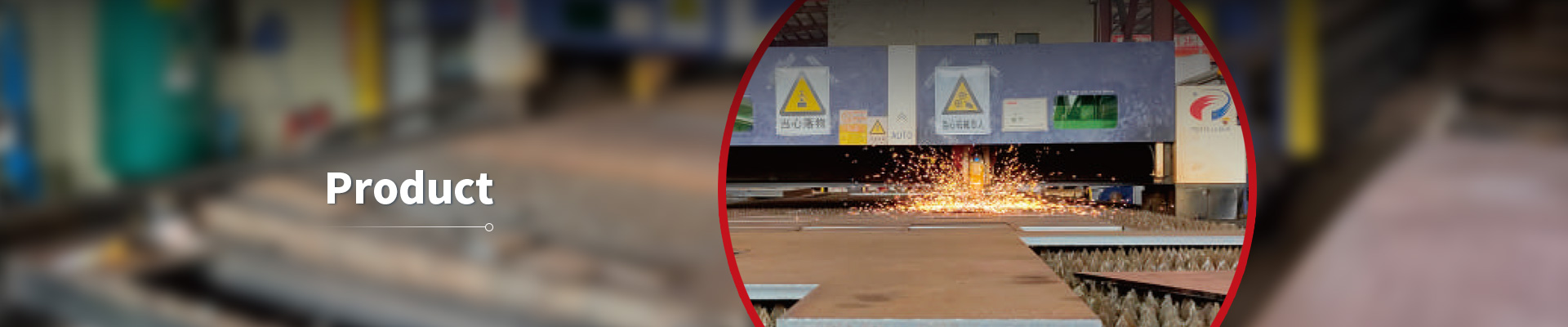
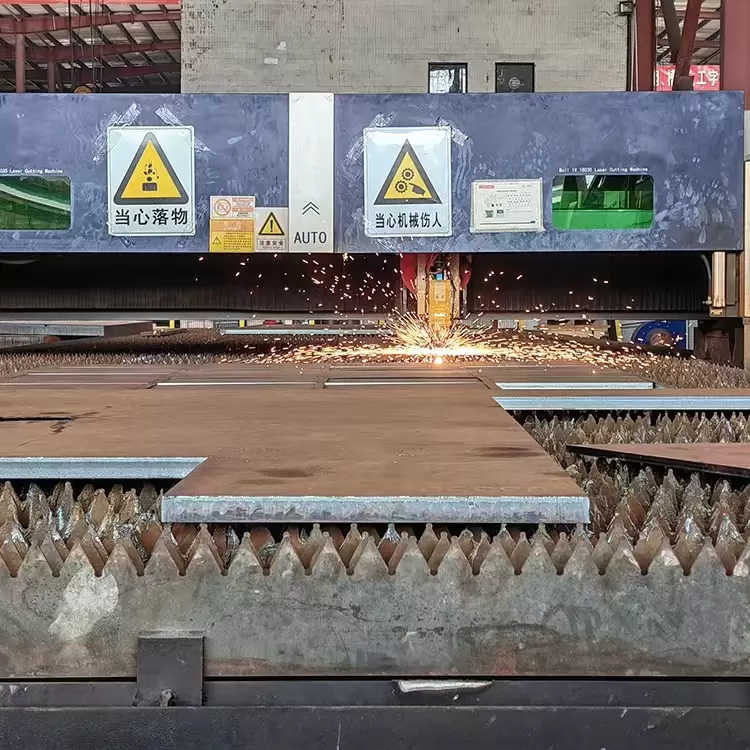
CNC cutting
 0757-28908555
0757-28908555
How CNC Cutting Works
The core of CNC cutting lies in its integration of digital design and automated execution:
1. Design Input: Engineers create 2D or 3D part designs using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software (e.g., AutoCAD, SolidWorks).
2. Program Generation: CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software converts the design into G-code—a numerical language that specifies cutting paths, speeds, and tool parameters.
3. Automated Cutting: The CNC machine interprets the G-code, adjusting the cutting head’s position, angle, and feed rate in real time to execute the cut with minimal human intervention.
Types of CNC Cutting Technologies
Different CNC cutting methods are tailored to specific materials, thicknesses, and precision requirements:
1. CNC Plasma Cutting
· Principle: Uses a high-temperature plasma arc (15,000–30,000°C) to melt and blow away metal, enabling fast, clean cuts.
· Applications: Ideal for carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and non-ferrous metals with thicknesses ranging from 0.5mm to 100mm.
· Advantages: High cutting speed (3–5 times faster than flame cutting), good precision (tolerance ±0.5mm), and versatility across materials.
· Best For: Medium-to-thick plates, batch production of structural parts, and industries requiring quick turnaround (e.g., construction, automotive).
2. CNC Laser Cutting
· Principle: Focuses a high-energy laser beam on the material surface, melting, vaporizing, or burning through the metal with extreme precision.
· Applications: Suits thin to medium sheets (0.1mm–20mm) of steel, stainless steel, brass, and copper.
· Advantages: Exceptional precision (tolerance ±0.1mm), smooth, burr-free edges, minimal heat-affected zone (reducing material distortion), and ability to cut intricate patterns (e.g., fine holes, complex curves).
· Best For: High-precision components, decorative metalwork, and industries like aerospace and electronics.
3. CNC Flame Cutting
· Principle: Uses oxy-fuel combustion (e.g., oxygen + acetylene) to generate intense heat (≈3,000°C), melting thick metal for cutting.
· Applications: Primarily for carbon steel and low-alloy steel with thicknesses ≥20mm (up to several hundred millimeters).
· Advantages: Low equipment cost, high efficiency for thick plates, and suitability for large structural parts.
Best For: Heavy machinery, shipbuilding, and bridge construction where precision requirements are moderate (tolerance ±1mm).
RELATED PRODUCTS
Products
-
No Data




