Product
Contact us




CNC cutting
 0757-28908555
0757-28908555
Core Technology and Equipment Types
The core of CNC cutting lies in "program control" — generating part graphics through CAD drawing software, which are then converted into G-code recognizable by cutting equipment via a CAM system. The equipment automatically adjusts the walking trajectory, speed, and cutting parameters of the cutting head according to the code, realizing full-process automated operation. According to different cutting principles and applicable materials, mainstream equipment can be divided into the following categories:
· 1:CNC flame cutting: It uses the high temperature (about 3000℃) generated by the combustion of oxygen and fuel gas (such as acetylene, propane) to melt metal and complete cutting. It is suitable for medium and heavy steel plates (such as Q235, Q355 structural steel) with a thickness of more than 20mm. It has low cost and high cutting efficiency, but the precision is relatively low (generally ±1mm), making it suitable for processing large structural parts that do not require extreme precision.
·
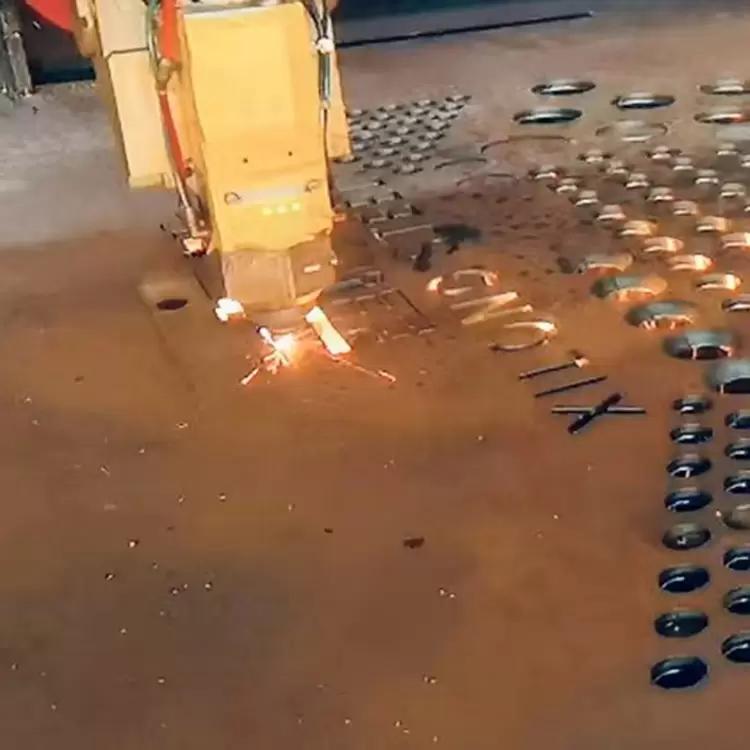
· 2:CNC plasma cutting: It instantly melts and blows away metal through a plasma arc (with a temperature up to 15000-30000℃). It is applicable to materials such as steel plates, stainless steel, and aluminum alloys with a thickness of 0.5-100mm. It has a fast cutting speed (3-5 times that of flame cutting) and high precision (±0.5mm), capable of handling fine cutting of thin plates and rapid processing of medium and heavy plates. It is one of the most widely used CNC cutting methods at present.
·
· 3:CNC laser cutting: It focuses a high-energy laser beam on the material surface, causing the material to instantly melt, vaporize, or burn. It is suitable for thin plates (such as stainless steel, carbon steel, non-ferrous metals) with a thickness of 0.1-20mm. The cutting precision can reach ±0.1mm, with smooth and burr-free cuts, minimal heat-affected zone, and the ability to process complex fine contours (such as precision gears, irregular holes). However, the equipment cost is relatively high, making it more suitable for high-precision and high-complexity processing needs.
·
In addition, there are special types such as CNC water jet cutting (suitable for heat-sensitive materials), which can be flexibly selected according to material characteristics and processing requirements.
Technical Advantages and Core Features
1:High Precision and Strong Consistency
CNC cutting precisely controls the cutting trajectory through computer programs, avoiding errors caused by manual operations. The cutting dimensional tolerance can be controlled within ±0.1-1mm (depending on the equipment type), and the dimensional consistency of mass-produced parts is extremely high, meeting the precise matching requirements for multi-component assembly. For example, in the processing of connectors for steel structure bridges, the hole position deviation of CNC cutting can be controlled within 0.5mm, ensuring seamless 对接 during installation.
2:High Efficiency and Reduced Labor Costs
The equipment can operate continuously 24 hours a day, with a cutting speed far exceeding that of manual work (e.g., plasma cutting can reach 5-10 meters per hour for medium and heavy steel plates). Without the need for real-time manual control, one operator can supervise multiple devices simultaneously, significantly increasing the processing volume per unit time and reducing labor costs and management difficulties.
3:High Flexibility and Adaptability to Complex Processing
Whether it is simple rectangular cutting, circular cutting, or processing of special-shaped parts with arcs, polylines, or bevels, the processing scheme can be quickly switched by simply modifying the program, without the need to replace molds or tooling. For instance, irregular hull ribs in shipbuilding and special-shaped flanges in mechanical parts can be formed in one go through CNC cutting, eliminating the need for secondary processing.
4:High Material Utilization and Reduced Waste
Advanced nesting software can optimize the layout of steel plates, tightly nesting multiple part graphics to maximize the use of raw materials. Compared with manual cutting, material utilization is increased by 10%-30%, which can significantly reduce material costs, especially for high-value steels (such as stainless steel and alloy steel plates).
5:Improved Safety and Environmental Protection
Automated operations reduce direct contact between workers and high temperatures and dust. Combined with dust removal systems and protective devices, they can effectively reduce the risk of work-related injuries and environmental pollution, complying with safety and environmental protection standards in modern industry.
RELATED PRODUCTS
Products
-
No Data




